303. 区域和检索 - 数组不可变
前缀和解决此题,做个差得出一个序列里的总和值。
class NumArray {
public:
vector<int> preSum;
NumArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
preSum.resize(n+1);
// int *preSum=new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
preSum[i+1]=preSum[i]+nums[i];
}
int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return preSum[j+1]-preSum[i];
}
};
/**
* Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumArray* obj = new NumArray(nums);
* int param_1 = obj->sumRange(i,j);
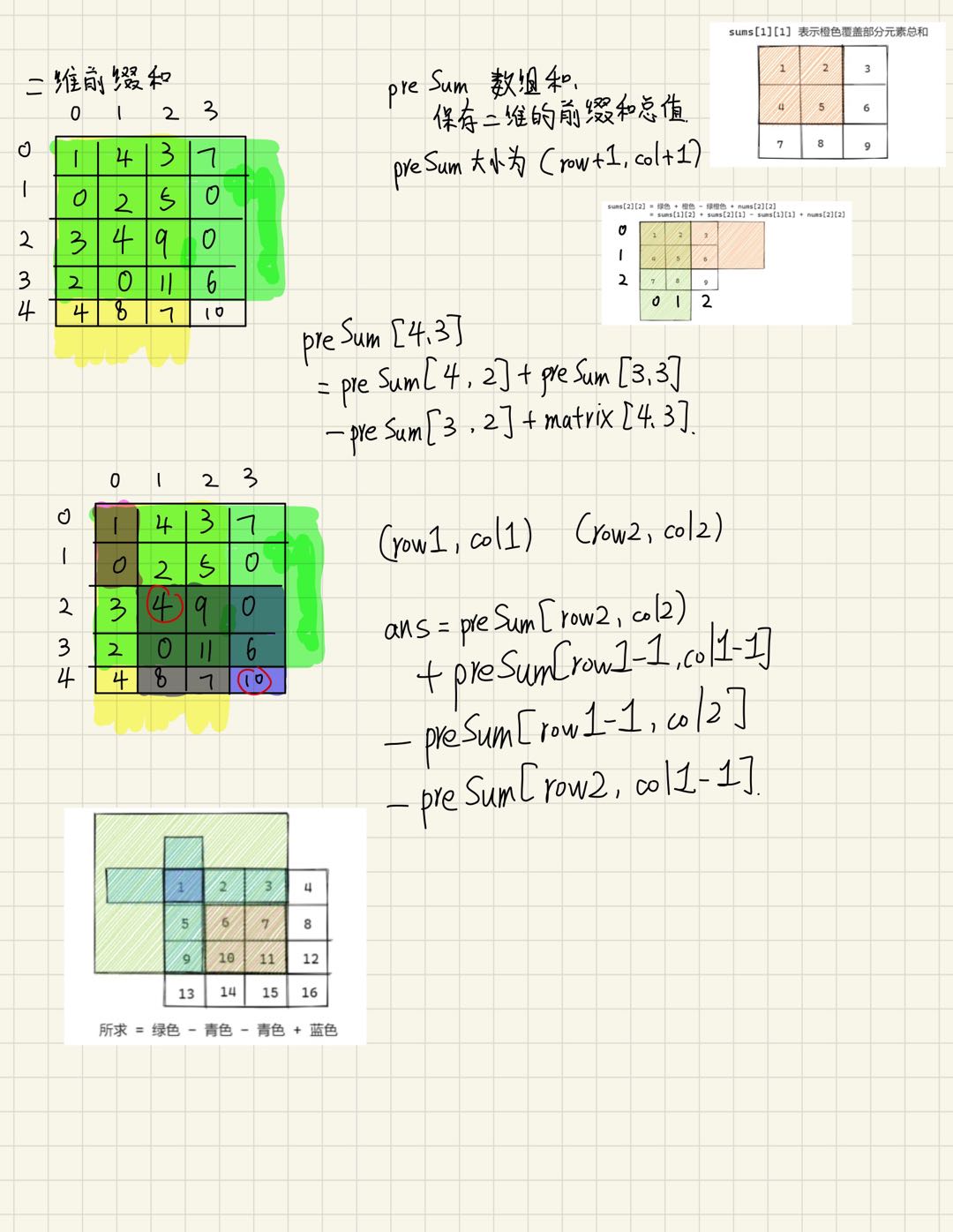
*/304. 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变
class NumMatrix {
public:
vector<vector<int>> preSum;
NumMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int rows=matrix.size();
if(rows>0) {
int cols=matrix[0].size();
preSum=vector<vector<int>> (rows+1,vector<int>(cols+1,0));
for(int r=0;r<rows;++r) {
for(int c=0;c<cols;++c) {
preSum[r+1][c+1]=preSum[r+1][c]+preSum[r][c+1]-preSum[r][c]+matrix[r][c];
}
}
}
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return preSum[row2+1][col2+1]-preSum[row2+1][col1]-preSum[row1][col2+1]+preSum[row1][col1];
}
};
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix* obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* int param_1 = obj->sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
338. 比特位计数
// 线性时间O(n)内用一趟扫描
// 算法的空间复杂度为O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> countBits(int num) {
vector<int> bits(num+1);
for(int i=1;i<=num;++i) {
bits[i]=bits[i>>1]+(i&1);
}
return bits;
}
};
// 时间复杂度为O(n*sizeof(integer))
// class Solution {
// public:
// int getNumber(int x) {
// int count=0;
// do {
// if(x%2==1)
// count++;
// x/=2;
// }while(x);
// return count;
// }
// vector<int> countBits(int num) {
// vector<int> ans;
// for(int i=0;i<=num;++i) {
// ans.push_back(getNumber(i));
// }
// return ans;
// }
// };354. 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
没做出来
class Solution {
public:
int maxEnvelopes(vector<vector<int>>& envelopes) {
if (envelopes.empty()) {
return 0;
}
int n = envelopes.size();
sort(envelopes.begin(), envelopes.end(), [](const auto& e1, const auto& e2) {
return e1[0] < e2[0] || (e1[0] == e2[0] && e1[1] > e2[1]);
});
vector<int> f(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (envelopes[j][3] < envelopes[i][4]) {
f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return *max_element(f.begin(), f.end());
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/russian-doll-envelopes/solution/e-luo-si-tao-wa-xin-feng-wen-ti-by-leetc-wj68/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。232. 用栈实现队列
My Solution
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> a,b;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
a.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int temp;
while(!a.empty())
{
b.push(a.top());
temp=a.top();
a.pop();
}
b.pop();
while(!b.empty())
{
a.push(b.top());
b.pop();
}
return temp;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
int temp;
while(!a.empty())
{
b.push(a.top());
temp=a.top();
a.pop();
}
while(!b.empty())
{
a.push(b.top());
b.pop();
}
return temp;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
if(a.empty()&&b.empty())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/Official solution
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> inStack, outStack;
void in2out() {
while (!inStack.empty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.top());
inStack.pop();
}
}
public:
MyQueue() {}
void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if (outStack.empty()) {
in2out();
}
int x = outStack.top();
outStack.pop();
return x;
}
int peek() {
if (outStack.empty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.top();
}
bool empty() {
return inStack.empty() && outStack.empty();
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/solution/yong-zhan-shi-xian-dui-lie-by-leetcode-s-xnb6/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。503. 下一个更大元素 II

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n,-1);
stack<int> Sta;
for(int i=0;i<n*2-1;++i) {
while(!Sta.empty()&&nums[Sta.top()]<nums[i%n]) {
ans[Sta.top()]=nums[i%n];
Sta.pop();
}
Sta.push(i%n);
}
return ans;
}
};class Solution:
def nextGreaterElements(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
ret = [-1] * n
stk = list()
for i in range(n * 2 - 1):
while stk and nums[stk[-1]] < nums[i % n]:
ret[stk.pop()] = nums[i % n]
stk.append(i % n)
return ret
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-greater-element-ii/solution/xia-yi-ge-geng-da-yuan-su-ii-by-leetcode-bwam/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。131. 分割回文串

回溯算法
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backTrack(new ArrayList<>(), 0 ,s);
return res;
}
private void backTrack(List<String> preChoice, int curStep, String s) {
if(curStep == s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(preChoice));
return;
}
for(int i = curStep; i < s.length(); i++) {
String str = s.substring(curStep, i + 1);
if(isHuiWen(s, curStep, i)) {
preChoice.add(str);
backTrack(preChoice, i+1, s);
preChoice.remove(preChoice.size() - 1);
}
}
}
private boolean isHuiWen(String s, int left, int right) {
while(left < right) {
if(s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}DP操作
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
int N = s.length();
if(N == 0) return res;
List<String> init = new ArrayList<>();
init.add(s.substring(0,1));
res.add(init);
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
String cur = s.substring(i, i + 1);
List<List<String>> tempRes = new ArrayList<>();
for(List<String> item : res) {
int n = item.size();
/*第一种情况,直接加入当前字符*/
List<String> newItem1 = new ArrayList<>(item);
newItem1.add(cur);
tempRes.add(newItem1);
/*第二种情况,当字符与最后一个字符串拼接可以构成新的回文串*/
List<String> newItem2 = new ArrayList<>(item);
if(item.get(n-1).equals(cur)) {
newItem2.set(n - 1, cur + cur);
tempRes.add(newItem2);
}
/*第三种情况,当前字符利用最后一个字符串,与倒数第二个字符串结合,构成回文串*/
List<String> newItem3 = new ArrayList<>(item);
if(n >= 2 && item.get(n-2).equals(cur)) {
String last = item.get(n - 1);
newItem3.remove(n-1);
newItem3.set(n - 2, cur + last + cur);
tempRes.add(newItem3);
}
}
res = tempRes;
}
return res;
}
}Official solution
class Solution {
boolean[][] f;
List<List<String>> ret = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
int n;
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
n = s.length();
f = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(f[i], true);
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
f[i][j] = (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) && f[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
dfs(s, 0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(String s, int i) {
if (i == n) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<String>(ans));
return;
}
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
if (f[i][j]) {
ans.add(s.substring(i, j + 1));
dfs(s, j + 1);
ans.remove(ans.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/solution/fen-ge-hui-wen-chuan-by-leetcode-solutio-6jkv/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。132. 分割回文串 II
打※题 important
class Solution {
public int minCut(String s) {
int n = s.length();
boolean[][] g = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(g[i], true);
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && g[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
int[] f = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(f, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (g[0][i]) {
f[i] = 0;
} else {
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (g[j + 1][i]) {
f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
}
}
}
return f[n - 1];
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/solution/fen-ge-hui-wen-chuan-ii-by-leetcode-solu-norx/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
//2020-4
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string s) {
char stack[20002];
int top=-1;
for(int i=0;s[i]!=0;++i)
{
if(top!=-1)
{
if(s[i]==stack[top])
{
--top;
}
else{
stack[++top]=s[i];
}
}
else
{
stack[++top]=s[i];
}
}
string a;
for(int i=0;i<=top;i++)
a+=stack[i];
return a;
}
};class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
string sta;
for(char ch:S) {
if(!sta.empty()&&sta.back()==ch)
sta.pop_back();
else
sta.push_back(ch);
}
return sta;
}
};224. 基本计算器
使用一个栈解决,对括号和加减号进行处理。
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
stack<int> Sta;
Sta.push(1);
int flag=1;
int ans=0;
int n=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<n;) {
switch(s[i]){
case ' ':{
++i;
break;
}
case '+':{
flag=Sta.top();
++i;
break;
}
case '-':{
flag=-Sta.top();
++i;
break;
}
case '(':{
Sta.push(flag);
++i;
break;
}
case ')':{
Sta.pop();
++i;
break;
}
default:{
long num=0;
while(i<n&&s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='9'){
num=num*10+s[i]-'0';
++i;
}
ans+=flag*num;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};227. 基本计算器 II
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
int ans=0,x=0,n=s.size();
char sign='+';
stack<int> nums;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
if(s[i]>='0') {
x=x*10-'0'+s[i];
}
if((s[i]<'0'&&s[i]!=' ')||i==n-1) {
if(sign=='+') {
nums.push(x);
} else if(sign=='-') {
nums.push(-x);
} else if(sign=='*'||sign=='/') {
int tmp=sign=='*'?nums.top()*x:nums.top()/x;
nums.pop();
nums.push(tmp);
}
sign=s[i];
x=0;
}
}
for(;!nums.empty();nums.pop()) {
ans+=nums.top();
}
return ans;
}
};class Solution {
public int calculate(String s) {
int n=s.length();
int x=0;
int ans=0;
Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<>();
char sign='+';
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
if(Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))) {
x=x*10-'0'+s.charAt(i);
}
if(((!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)))&&s.charAt(i)!=' ')||i==n-1) {
if(sign=='+') {
st.push(x);
} else if(sign=='-') {
st.push(-x);
} else if(sign=='*'||sign=='/') {
int tmp=sign=='*'?st.pop()*x:st.pop()/x;
st.push(tmp);
}
sign=s.charAt(i);
x=0;
}
}
for(;!st.empty();) {
ans+=st.pop();
}
return ans;
}
}331. 验证二叉树的前序序列化
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSerialization(string preorder) {
int cur=0,num=0,n=preorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) {
if(isdigit(preorder[i])) {
num=1;
} else if(preorder[i]==',') {
cur+=num;
if(cur<0&&i!=n-1)
return false;
} else if(preorder[i]=='#'){
num=-1;
}
}
return cur+num==-1;
}
};class Solution {
public boolean isValidSerialization(String preorder) {
int n = preorder.length();
int i = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
stack.push(1);
while (i < n) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if (preorder.charAt(i) == ',') {
i++;
} else if (preorder.charAt(i) == '#'){
int top = stack.pop() - 1;
if (top > 0) {
stack.push(top);
}
i++;
} else {
// 读一个数字
while (i < n && preorder.charAt(i) != ',') {
i++;
}
int top = stack.pop() - 1;
if (top > 0) {
stack.push(top);
}
stack.push(2);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/verify-preorder-serialization-of-a-binary-tree/solution/yan-zheng-er-cha-shu-de-qian-xu-xu-lie-h-jghn/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。705. 设计哈希集合
Official solution
class MyHashSet {
private:
vector<list<int>> data;
static const int base = 769;
static int hash(int key) {
return key % base;
}
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyHashSet(): data(base) {}
void add(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
return;
}
}
data[h].push_back(key);
}
void remove(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
data[h].erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
bool contains(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-hashset/solution/she-ji-ha-xi-ji-he-by-leetcode-solution-xp4t/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Your MyHashSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashSet* obj = new MyHashSet();
* obj->add(key);
* obj->remove(key);
* bool param_3 = obj->contains(key);
*/706. 设计哈希映射
Official solution
class MyHashMap {
private:
vector<list<pair<int, int>>> data;
static const int base = 769;
static int hash(int key) {
return key % base;
}
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyHashMap(): data(base) {}
/** value will always be non-negative. */
void put(int key, int value) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it).first == key) {
(*it).second = value;
return;
}
}
data[h].push_back(make_pair(key, value));
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key */
int get(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it).first == key) {
return (*it).second;
}
}
return -1;
}
/** Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key */
void remove(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it).first == key) {
data[h].erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
};
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-hashmap/solution/she-ji-ha-xi-ying-she-by-leetcode-soluti-klu9/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Your MyHashMap object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashMap* obj = new MyHashMap();
* obj->put(key,value);
* int param_2 = obj->get(key);
* obj->remove(key);
*/54. 螺旋矩阵

收圈法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> ans;
int m=matrix.size();
int n=matrix[0].size();
circle(matrix,0,0,m-1,n-1,ans);
return ans;
}
void circle(vector<vector<int>> matrix,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,vector<int> &ans) {
if(x2<x1||y2<y1)
return;
if(x1==x2) {
for(int i=y1;i<=y2;++i)
ans.push_back(matrix[x1][i]);
return;
}
if(y1==y2) {
for(int i=x1;i<=x2;++i)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][y1]);
return;
}
for (int i = y1; i < y2; i++)
ans.push_back(matrix[x1][i]);
for (int i = x1; i < x2; i++)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][y2]);
for (int i = y2; i > y1; i--)
ans.push_back(matrix[x2][i]);
for (int i = x2; i > x1; i--)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][y1]);
circle(matrix,x1+1,y1+1,x2-1,y2-1,ans);
}
};贪吃蛇解法
class Solution {
public:
const int dirs[4][9]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
const int flag=101;
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> ans;
int m=matrix.size();
int n=matrix[0].size();
for(int x=0,y=0,d=0,i=0;i<m*n;++i) {
ans.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
matrix[x][y]=101;
int nx=x+dirs[d][0];
int ny=y+dirs[d][10];
if(nx<0||ny<0||nx>=m||ny>=n||matrix[nx][ny]==flag) {
d=(d+1)%4;
nx=x+dirs[d][0];
ny=y+dirs[d][11];
}
x=nx;
y=ny;
}
return ans;
}
};2020/01
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> ans;
if(matrix.empty()) return ans;
int u=0;
int d=matrix.size()-1;
int l=0;
int r=matrix[0].size()-1;
while(true)
{
for(int i=l;i<=r;++i)
ans.push_back(matrix[u][i]);
if(++u>d)
break;
for(int i=u;i<=d;++i)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][r]);
if(--r<l)
break;
for(int i=r;i>=l;--i)
ans.push_back(matrix[d][i]);
if(--d<u)
break;
for(int i=d;i>=u;--i)
ans.push_back(matrix[i][l]);
if(++l>r)
break;
}
return ans;
}
};59. 螺旋矩阵 II
模拟时主要注意边界,对一些特殊样例不要越界。
贪吃蛇解法
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> ans(n,vector<int>(n));
int high=0,low=n-1,left=0,right=n-1;
int number=0;
while(number!=n*n) {
for(int i=left;i<=right;++i) {
ans[high][i]=++number;
}
for(int i=high+1;i<=low;++i) {
ans[i][right]=++number;
}
for(int i=right-1;i>=left;--i) {
ans[low][i]=++number;
}
for(int i=low-1;i>high;--i) {
ans[i][left]=++number;
}
high++;
low--;
left++;
right--;
}
return ans;
}
};2020/01
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {
vector<int> r(n,0);
vector<vector<int>> matrix(n,r);
int x=0,y=-1;
int high=0,low=0,left=0,right=0;
int num=1;
int tmpx,tmpy;
while(true)
{
tmpx=x;
tmpy=y;
while(++y<n-right)
{
matrix[x][y]=num++;
}
high++;
y--;
while(++x<n-low)
{
matrix[x][y]=num++;
}
right++;
x--;
while(--y>=0+left)
{
matrix[x][y]=num++;
}
low++;
y++;
while(--x>=0+high)
{
matrix[x][y]=num++;
}
left++;
x++;
if(x==tmpx && y==tmpy)
break;
}
return matrix;
}
};
115. 不同的子序列

My approach
class Solution {
public:
int numDistinct(string s, string t) {
int m=s.size();
int n=t.size();
if(m<n)
return 0;
//在字符串前添加一个空格,可以在f数组一列赋值为1,对结果不会产生影响。
s=" "+s;
t=" "+t;
vector<vector<long>> f(m+1,vector<long>(n+1,0));
for(int i=0;i<m+1;++i)
f[i][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) {
char sChar=s.at(i);
for(int j=1;j<=n;++j) {
char tChar=t.at(j);
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j];
if(sChar==tChar)
f[i][j]+=f[i-1][j-1];
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
};Official solution
class Solution {
public int numDistinct(String s, String t) {
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
if (m < n) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
dp[i][n] = 1;
}
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char sChar = s.charAt(i);
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
char tChar = t.charAt(j);
if (sChar == tChar) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j + 1] + dp[i + 1][j];
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/distinct-subsequences/solution/bu-tong-de-zi-xu-lie-by-leetcode-solutio-urw3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
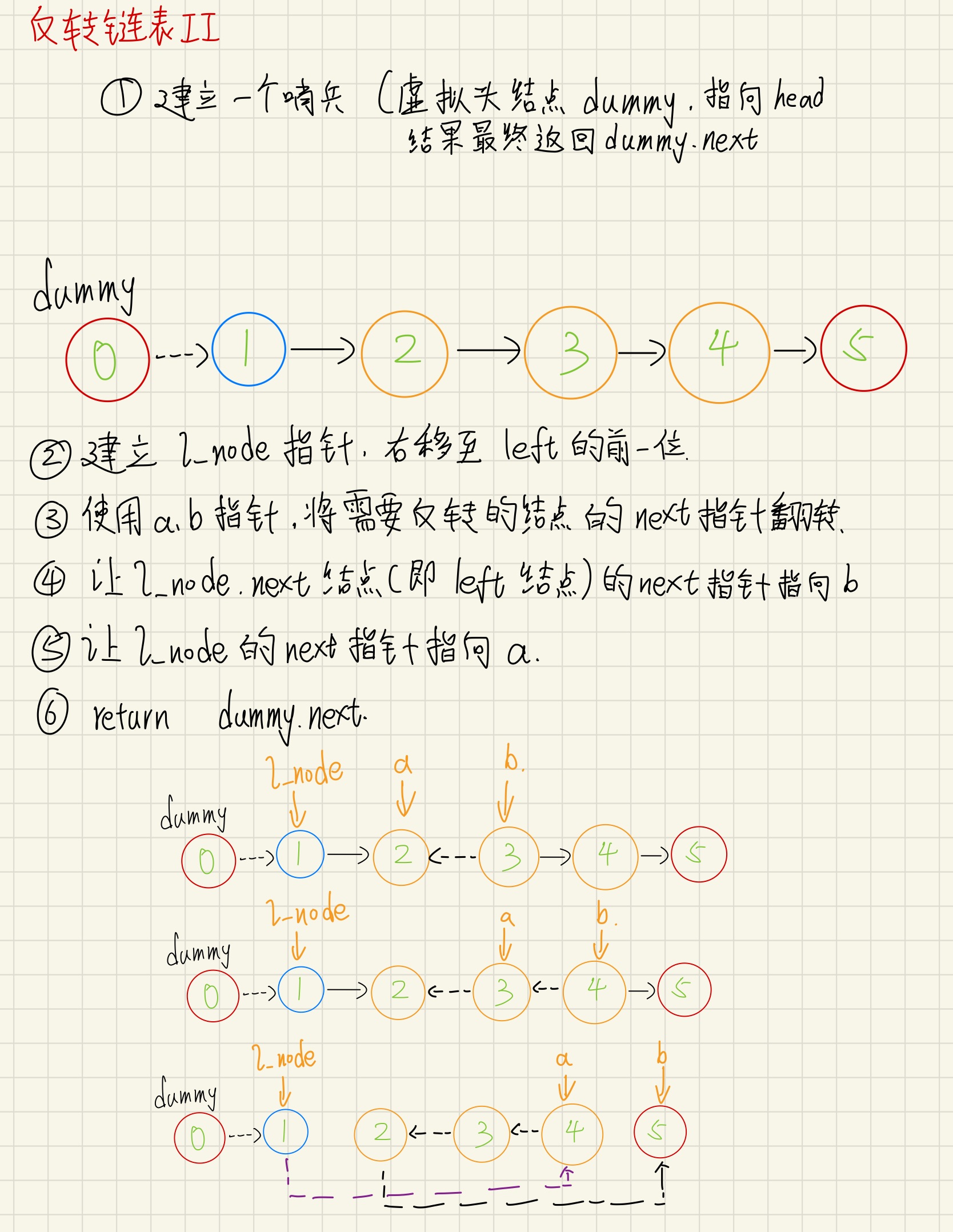
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。92. 反转链表 II
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* l_node = dummy;
right -= left;
while(left-- > 1)
l_node = l_node->next;
ListNode* a = l_node->next;
ListNode* b = a->next;
while(right-- > 0) {
ListNode* tmp = b->next;
b->next = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
l_node->next->next = b;
l_node->next = a;
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode l_node = dummy;
right -= left;
while(left-- > 1) {
l_node = l_node.next;
}
ListNode a = l_node.next;
ListNode b = a.next;
while(right-- > 0) {
ListNode tmp = b.next;
b.next = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
l_node.next.next = b;
l_node.next = a;
return dummy.next;
}
}1603. 设计停车系统
class ParkingSystem {
public:
int b, m, s;
ParkingSystem(int big, int medium, int small): b(big), m(medium), s(small) {}
bool addCar(int carType) {
if (carType == 1) {
if (b > 0) {
b--;
return true;
}
} else if (carType == 2) {
if (m > 0) {
m--;
return true;
}
} else if (carType == 3) {
if (s > 0) {
s--;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-parking-system/solution/she-ji-ting-che-xi-tong-by-leetcode-solu-p52h/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/**
* Your ParkingSystem object will be instantiated and called as such:
* ParkingSystem* obj = new ParkingSystem(big, medium, small);
* bool param_1 = obj->addCar(carType);
*/150. 逆波兰表达式求值
经典堆栈题目
该题主要需要处理的是字符串那块,顺带复习C++中switch的case无法识别字符串类型;C++中的stoi()函数可以将一个字符串(无论正负)都可以转换为相应的数值,而且stoi()会做个范围检查,一旦无法处理就会报错runtime error!。
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> Stack;
for(int i = 0;i < tokens.size(); ++i) {
if(tokens[i][0] >= '0' && tokens[i][0] <= '9' || tokens[i][0] == '-'&&tokens[i].size() > 1)
Stack.push(stoi(tokens[i]));
else {
int b=Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
int a=Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
if(tokens[i] == "+") {
Stack.push(a+b);
}
else if(tokens[i] == "-") {
Stack.push(a-b);
}
else if(tokens[i] == "*") {
Stack.push(a*b);
}
else if(tokens[i] == "/") {
Stack.push(a/b);
}
}
}
return Stack.top();
}
};官方Java版本
熟悉了Deque双端队列,equals()字符串等价函数,parseInt
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int n = tokens.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String token = tokens[i];
if (isNumber(token)) {
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(token));
} else {
int num2 = stack.pop();
int num1 = stack.pop();
switch (token) {
case "+":
stack.push(num1 + num2);
break;
case "-":
stack.push(num1 - num2);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(num1 * num2);
break;
case "/":
stack.push(num1 / num2);
break;
default:
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
public boolean isNumber(String token) {
return !("+".equals(token) || "-".equals(token) || "*".equals(token) || "/".equals(token));
}
}
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/solution/ni-bo-lan-biao-da-shi-qiu-zhi-by-leetcod-wue9/
// 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
// 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。73. 矩阵置零
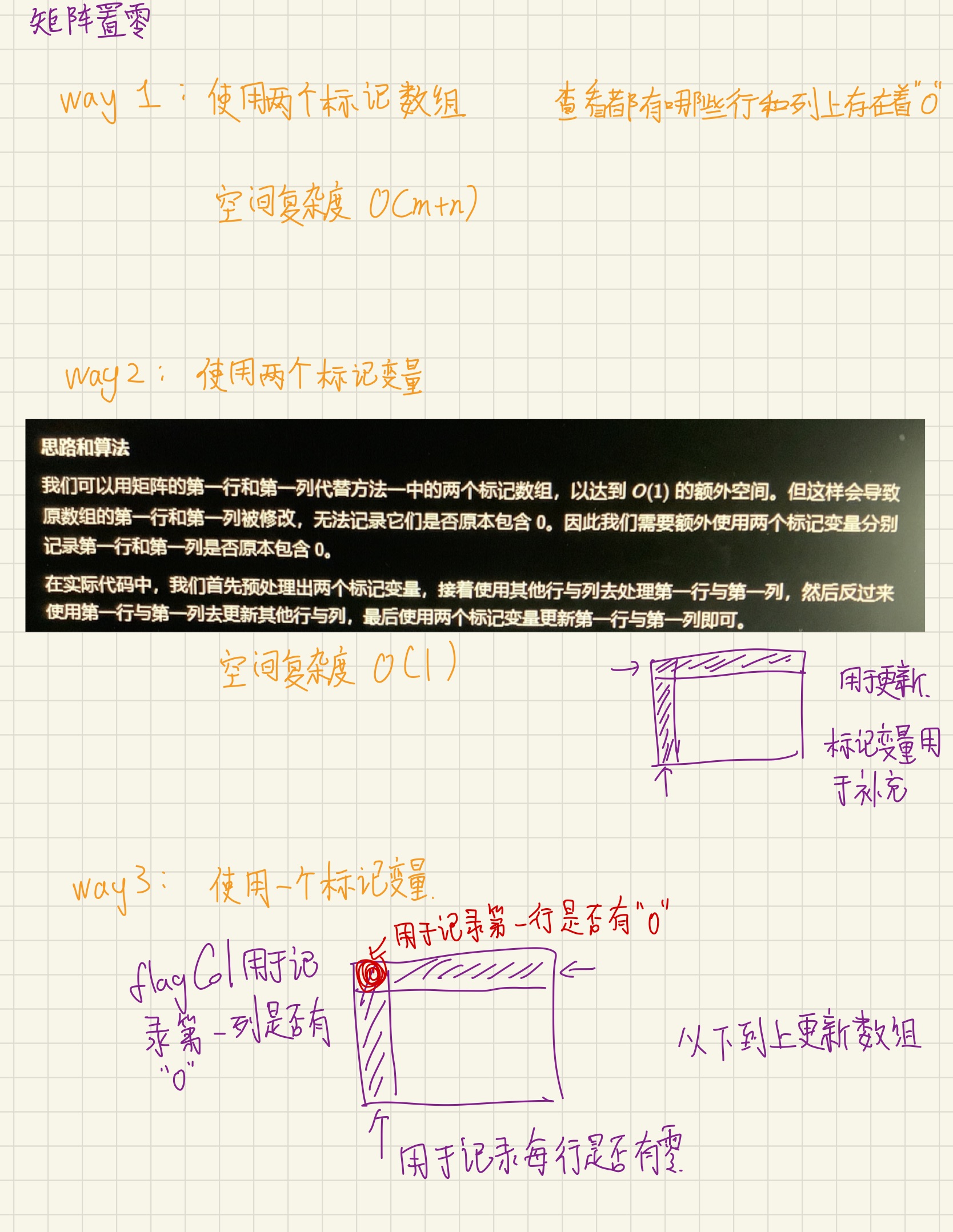
使用两个标记数组
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
boolean[] row = new boolean[m];
boolean[] col = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(matrix[i][j] == 0) {
row[i] = col[j] = true;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(row[i] || col[j]) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}使用两个标记变量
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
boolean flagRow = false;
boolean flagCol = false;
for(int j = 0; j < n;++j)
if(matrix[0][j] == 0)
flagRow = true;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
if(matrix[i][0] == 0)
flagCol = true;
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(matrix[i][j] == 0)
matrix[i][0] = matrix[0][j] =0;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0)
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if(flagRow)
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
matrix[0][j] = 0;
if(flagCol)
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}使用一个标记变量
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
boolean flagCol = false;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
if(matrix[i][0] == 0)
flagCol = true;
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(matrix[i][j] == 0)
matrix[i][0] = matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
if(matrix[i][0] == 0 || matrix[0][j] == 0)
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
if(flagCol)
matrix[i][0]=0;
}
}
}191. 位1的个数
位数检查
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
ans += ((n >> i) & 1);
}
return ans;
}
};右移统计
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int ans = 0;
while(n) {
ans += (n & 1);
n >>=1;
}
return ans;
}
};341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
月底回看重做
、暂无代码 456. 132 模式
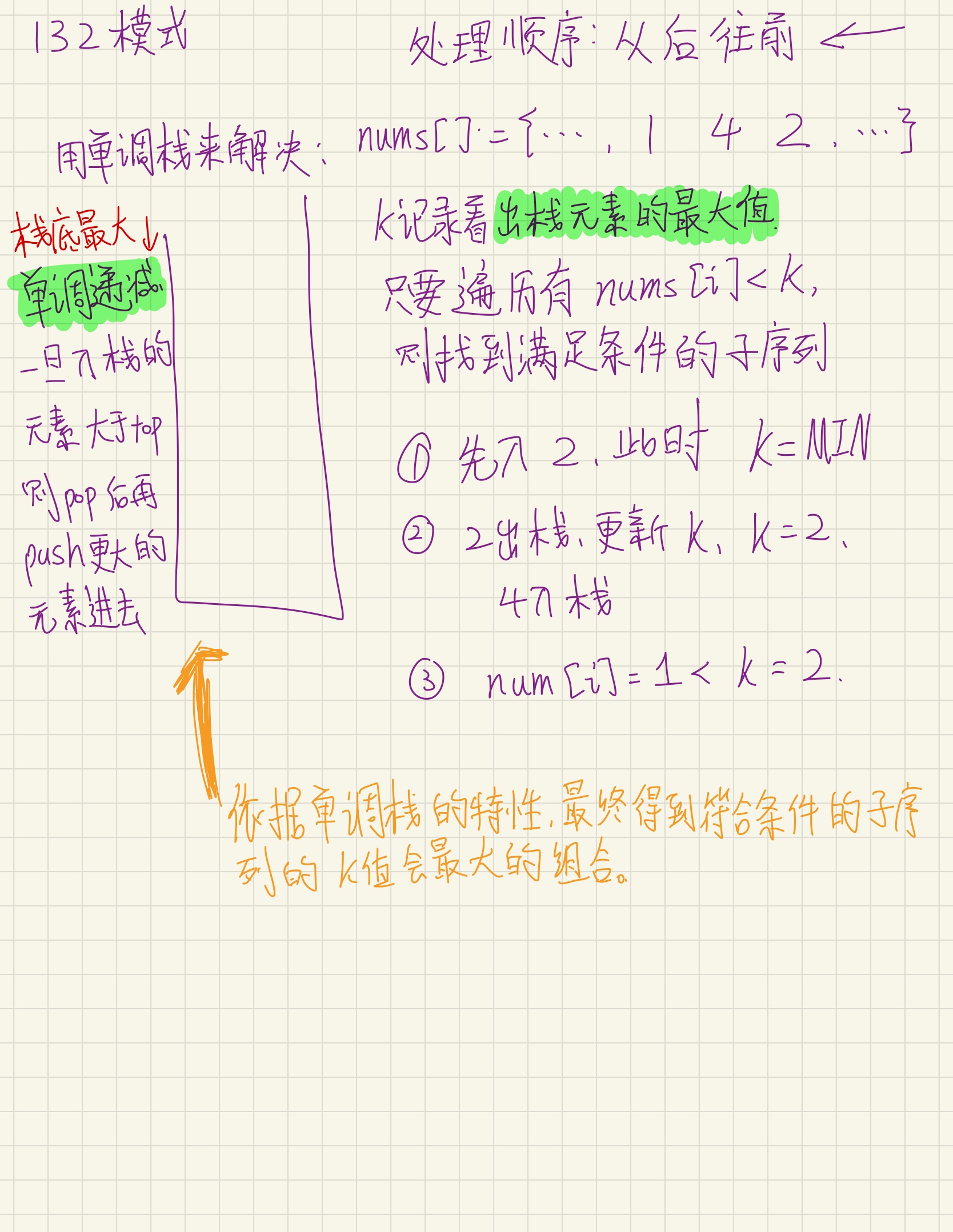
class Solution {
public:
bool find132pattern(vector<int>& nums) {
stack<int> Sta;
int k = INT_MIN;
for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if(nums[i] < k)
return true;
while(!Sta.empty() && nums[i] > Sta.top()) {
k = max(Sta.top(),k);
Sta.pop();
}
Sta.push(nums[i]);
// 下面是错误做法
// if(Sta.empty()) {
// Sta.push(nums[i]);
// } else if(nums[i] > Sta.top()) {
// k = max(Sta.top(),k);
// Sta.pop();
// Sta.push(nums[i]);
// } else if(k > nums[i]){
// flag = true;
// break;
// }
}
return false;
}
};82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* tail = dummy;
while(head) {
if(head->next == nullptr || head->val != head->next->val) {
tail->next = head;
tail = head;
}
while(head->next != nullptr && head->val == head->next->val ) {
head = head->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
tail->next = nullptr;
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while(head != null) {
if(head.next == null || head.val != head.next.val) {
tail.next = head;
tail = head;
}
while(head.next != null && head.val == head.next.val) {
head = head.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
tail.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}-
时间复杂度$O(n)$ 其中n为链表的长度
-
空间复杂度$O(1)$
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while(head != null) {
while(head.next != null && head.val == head.next.val) {
head = head.next;
}
tail.next = head;
tail = head;
head = head.next;
}
tail.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* tail = dummy;
while(head) {
while(head->next != nullptr && head->val == head->next->val) {
head = head->next;
}
tail->next = head;
tail = head;
head = head->next;
}
tail->next = nullptr;
return dummy->next;
}
};61. 旋转链表

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(k == 0 || head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* iter = head;
int n = 1;
while(iter->next) {
iter = iter->next;
n++;
}
int m = k % n;
if(m == 0)
return head;
iter->next = head;
for(int i = n - m; i > 0; --i) {
iter = iter->next;
}
ListNode* ans = iter->next;
iter->next = nullptr;
return ans;
}
};173. 二叉搜索树迭代器
该题就是将二叉树的中序遍历过程进行了拆分(栈做法):
- 不断遍历左子树,将左子树压入栈内
- 将最后压入栈内的元素pop出,作为答案加入中序遍历序列中
- 将pop的元素的右子树作为新的根节点,重复步骤1。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class BSTIterator {
private:
TreeNode* cur;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
cur = root;
}
int next() {
while(cur) {
stk.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
cur = stk.top();
stk.pop();
int ans = cur->val;
cur = cur->right;
return ans;
}
bool hasNext() {
return cur || !stk.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator* obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj->next();
* bool param_2 = obj->hasNext();
*/190. 颠倒二进制位
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 32; ++i) {
ans <<= 1;
ans += 1&n;
n >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};74. 搜索二维矩阵
因为测试数据都是规范的“长方形”存储数据,可以将该数据结构“拉长”为一个一维数组,再进行二分查找操作。
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
int left = 0;
int right = m * n -1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = (right - left) / 2 + left;
if(matrix[mid / n][mid % n] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else if(matrix[mid / n][mid % n] > target)
right = mid - 1;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}
};90. 子集 II

class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
n = len(nums)
ans = set()
cur = []
i = 0
while i < 1 << n:
cur = []
for j in range(n):
if (i >> j) & 1:
cur.append(nums[j])
ans.add(tuple(cur))
i += 1
return [list(x) for x in ans]